5 Ways UCSC is Revolutionizing Organoid Research

Unlocking the Secrets of Human Biology: 5 Ways UCSC is Revolutionizing Organoid Research

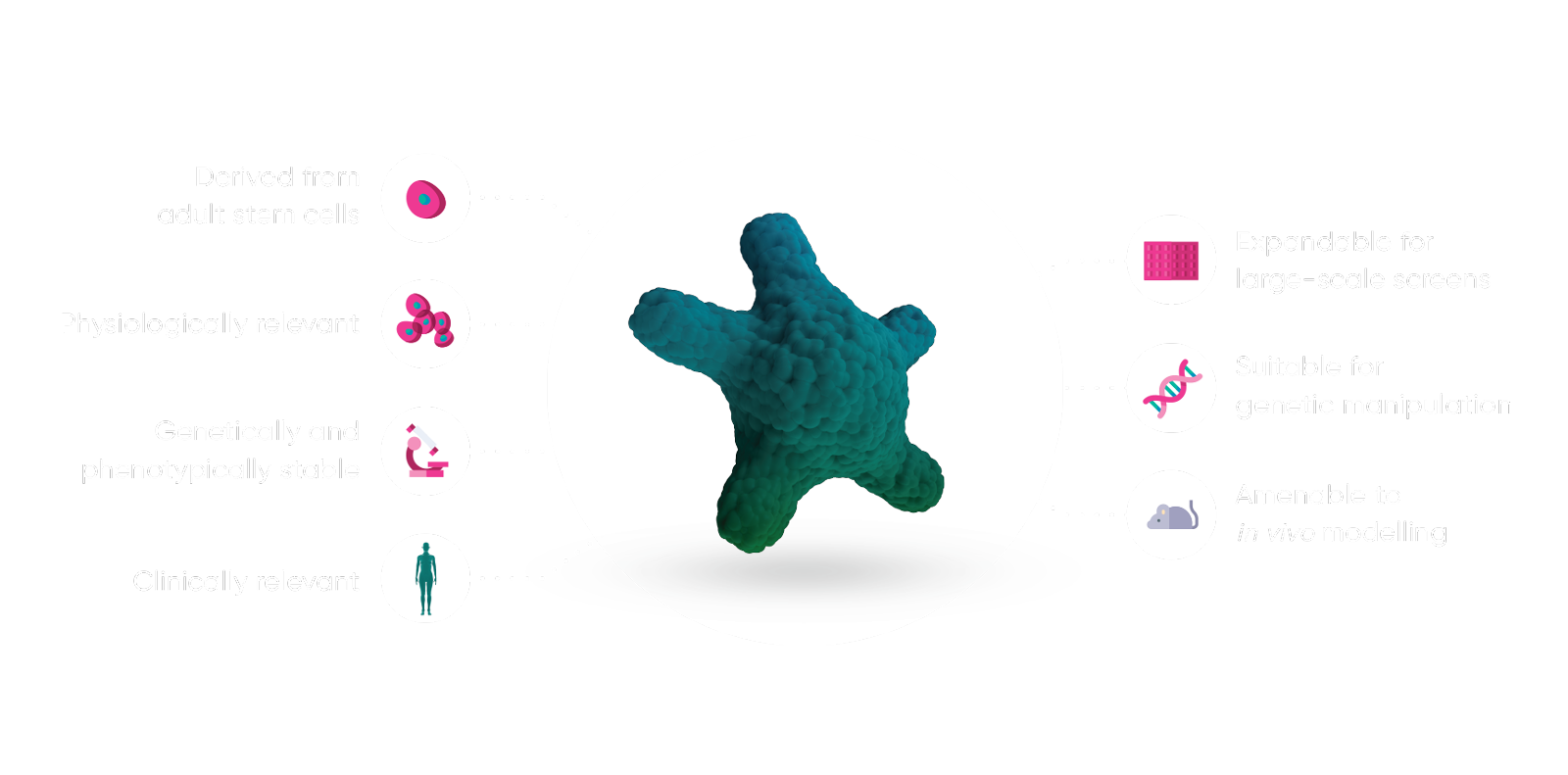
The field of organoid research has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, and the University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC) is at the forefront of this revolution. Organoids, three-dimensional cultures of cells that mimic the structure and function of organs, have opened up new avenues for understanding human biology and disease. UCSC researchers are pushing the boundaries of organoid technology, and their innovative approaches are transforming our understanding of human health and disease.
1. Brain Organoids: Modeling Neurological Disorders

UCSC researchers are using brain organoids to study neurological disorders such as autism, schizophrenia, and Alzheimer’s disease. By generating brain organoids from human stem cells, scientists can recapitulate the complex cellular interactions that occur during brain development and identify potential therapeutic targets. For instance, a study published in the journal Nature demonstrated the use of brain organoids to model the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to autism spectrum disorder.
🧠 Note: Brain organoids are not identical to actual brains, but they provide a valuable tool for understanding brain development and disease.
2. Organoid-Based Cancer Research: Personalized Medicine
UCSC researchers are utilizing organoids to study cancer biology and develop personalized treatment strategies. By generating organoids from patient-derived cancer cells, scientists can test the efficacy of different therapies and identify potential biomarkers for disease progression. For example, a study published in the journal Cancer Research demonstrated the use of organoids to predict treatment response in patients with colorectal cancer.
💊 Note: Organoid-based cancer research has the potential to revolutionize personalized medicine and improve treatment outcomes for patients.
3. Intestinal Organoids: Uncovering the Secrets of the Gut

UCSC researchers are using intestinal organoids to study the biology of the gut and its role in human health and disease. By generating intestinal organoids from human stem cells, scientists can investigate the complex interactions between the gut epithelium, immune system, and microbiome. For instance, a study published in the journal Nature Communications demonstrated the use of intestinal organoids to study the mechanisms of inflammatory bowel disease.
🌟 Note: Intestinal organoids provide a valuable tool for understanding the biology of the gut and its role in human health and disease.
4. Kidney Organoids: Modeling Kidney Development and Disease

UCSC researchers are using kidney organoids to study kidney development and disease. By generating kidney organoids from human stem cells, scientists can investigate the complex cellular interactions that occur during kidney development and identify potential therapeutic targets for kidney disease. For example, a study published in the journal Journal of the American Society of Nephrology demonstrated the use of kidney organoids to model the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to polycystic kidney disease.
🏥 Note: Kidney organoids provide a valuable tool for understanding kidney development and disease, and may lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
5. Organoid-Based Regenerative Medicine: Repairing Damaged Tissues

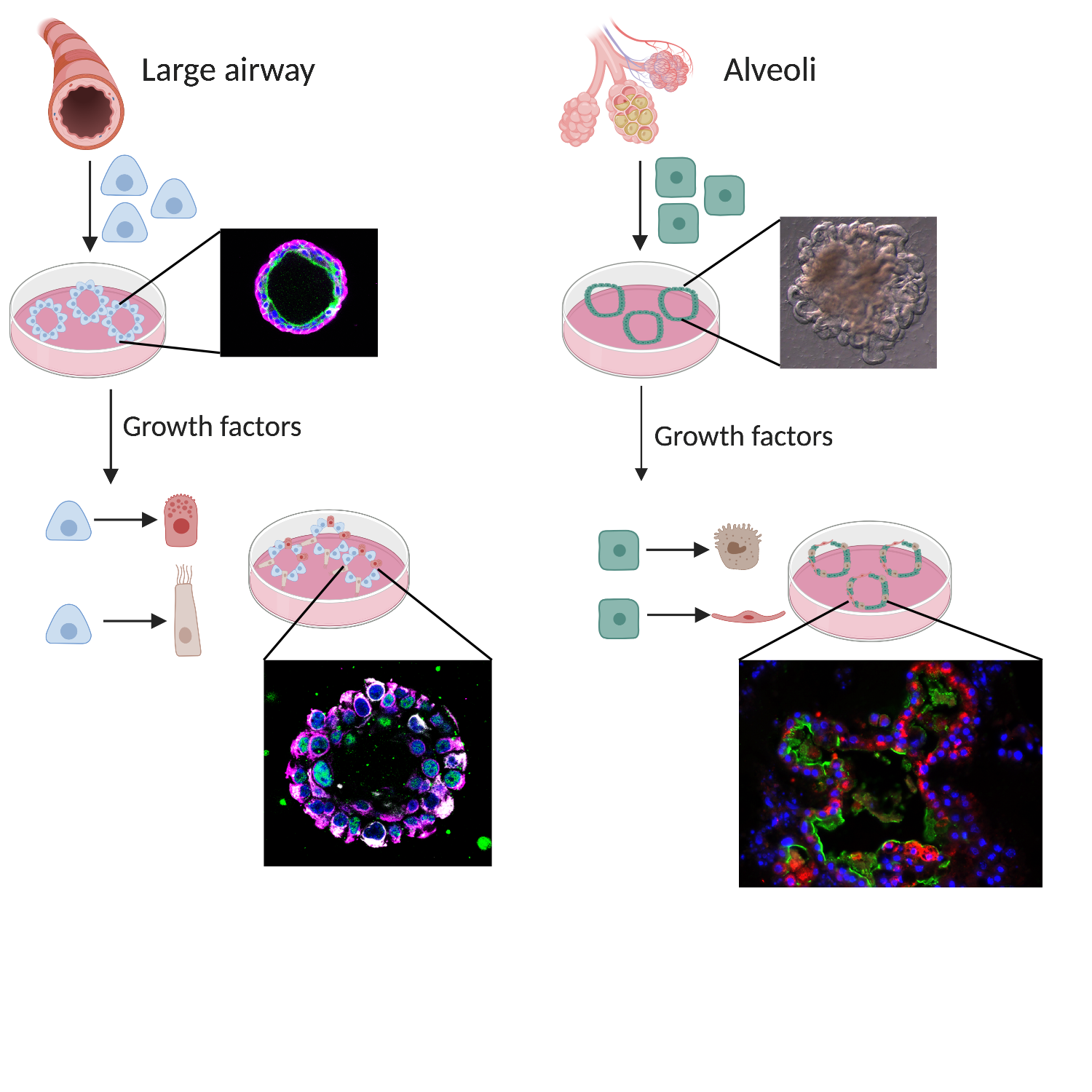
UCSC researchers are using organoids to develop novel regenerative medicine strategies for repairing damaged tissues. By generating organoids from human stem cells, scientists can create functional tissue substitutes that can be used to repair or replace damaged tissues. For instance, a study published in the journal Science Translational Medicine demonstrated the use of organoids to generate functional lung tissue for transplantation.
🔧 Note: Organoid-based regenerative medicine has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of damaged tissues and organs.
In conclusion, UCSC researchers are at the forefront of organoid research, and their innovative approaches are transforming our understanding of human biology and disease. From brain organoids to organoid-based regenerative medicine, the possibilities are endless, and the potential impact on human health is vast.
What are organoids?

+
Organoids are three-dimensional cultures of cells that mimic the structure and function of organs.
How are organoids used in research?

+
Organoids are used to study human biology and disease, develop personalized treatment strategies, and test the efficacy of different therapies.
What are the potential applications of organoid research?
+
The potential applications of organoid research include personalized medicine, regenerative medicine, and the development of novel therapeutic strategies for human disease.



