5 Ways to Become a US Air Force Pilot

Becoming a US Air Force Pilot: A Challenging yet Rewarding Career

The US Air Force is one of the most prestigious and technologically advanced air forces in the world, and becoming a pilot is a dream shared by many. However, the path to becoming a US Air Force pilot is challenging and requires a combination of academic excellence, physical fitness, and mental toughness. In this article, we will explore the different ways to become a US Air Force pilot and provide guidance on how to increase your chances of success.
Meet the Basic Requirements
Before we dive into the different ways to become a US Air Force pilot, it’s essential to meet the basic requirements. These include:
- Being a US citizen
- Being between the ages of 17 and 39 (with some exceptions for older candidates)
- Having a high school diploma or equivalent
- Scoring well on the Air Force Officer Qualifying Test (AFOQT)
- Passing a physical fitness test
- Having a valid driver’s license
💡 Note: Meeting the basic requirements is just the first step. The competition for pilot training slots is fierce, and only the most qualified candidates will be selected.
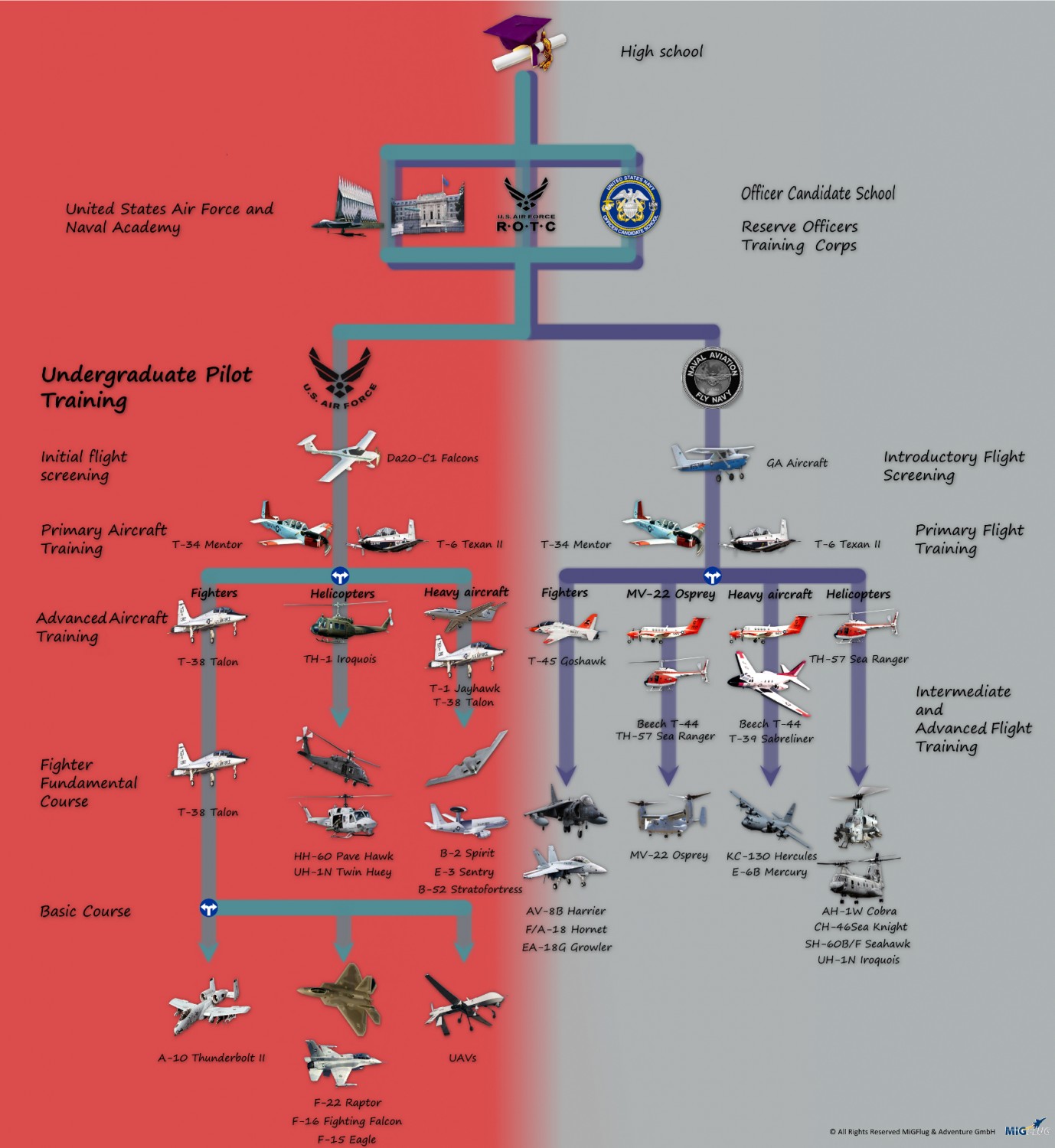
1. Attend the US Air Force Academy
One of the most prestigious ways to become a US Air Force pilot is to attend the US Air Force Academy in Colorado Springs, Colorado. The academy offers a four-year degree program that includes pilot training, and graduates are commissioned as second lieutenants in the Air Force.
- Pros: Free education, guaranteed pilot training slot, and a prestigious degree
- Cons: Highly competitive admission process, strict academic and physical standards
2. Attend a Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC) Program
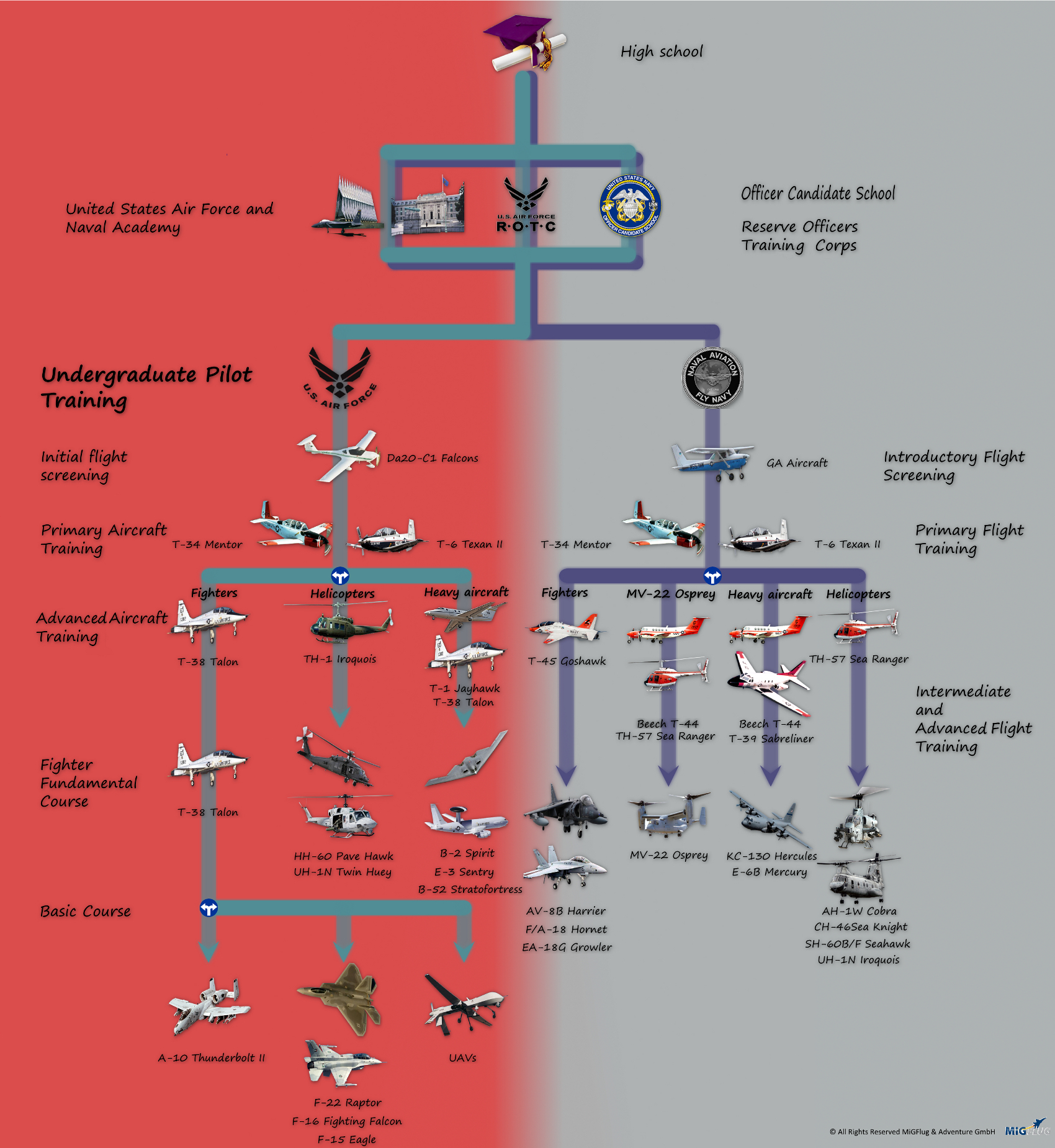
Another way to become a US Air Force pilot is to attend a ROTC program at a participating university. ROTC programs offer scholarships and stipends in exchange for a commitment to serve in the Air Force after graduation.
- Pros: Scholarships and stipends, flexible academic scheduling, and a guaranteed pilot training slot
- Cons: Competitive scholarship process, strict academic and physical standards
3. Attend Officer Training School (OTS)

OTS is a 12-week program that provides training for officers who have a bachelor’s degree from a non-ROTC program. OTS is a great option for those who have a degree in a field other than aviation.
- Pros: Flexible scheduling, opportunity to learn alongside other officers
- Cons: No guaranteed pilot training slot, competitive selection process
4. Join the Air National Guard or Air Force Reserve
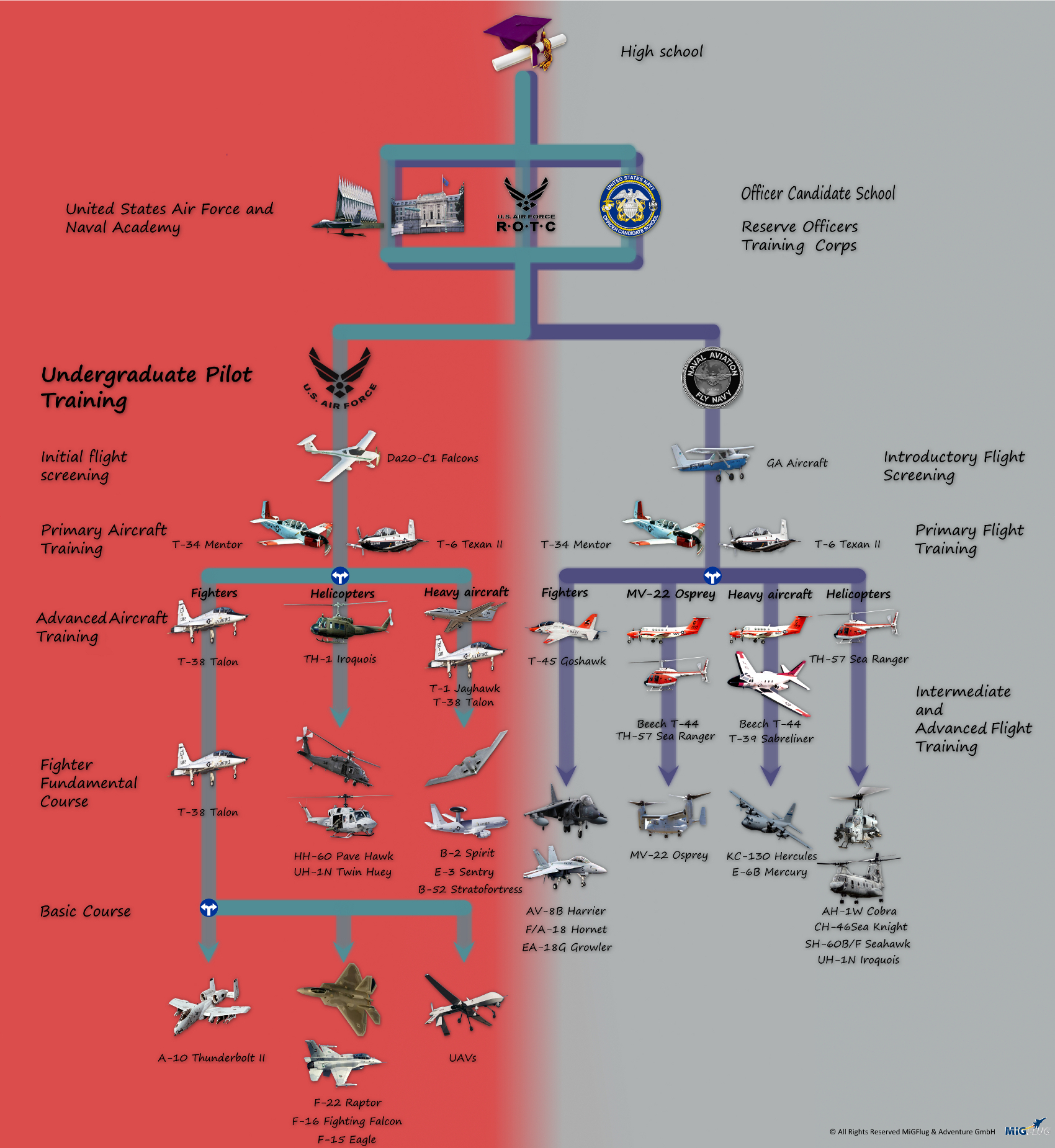
The Air National Guard and Air Force Reserve offer pilot training programs for those who want to serve part-time. These programs offer flexible scheduling and a chance to fly a variety of aircraft.
- Pros: Flexible scheduling, opportunity to fly a variety of aircraft, and a chance to serve part-time
- Cons: Limited pilot training slots, strict academic and physical standards
5. Attend a Civilian Flight School

Finally, it’s possible to attend a civilian flight school and earn a private pilot’s license. While this route does not guarantee a pilot training slot in the Air Force, it can be a great way to gain flying experience and increase your chances of being selected.
- Pros: Flexible scheduling, opportunity to gain flying experience, and a chance to build your skills
- Cons: No guaranteed pilot training slot, expensive tuition fees
🚀 Note: Becoming a US Air Force pilot requires a long-term commitment to serving in the military. It's essential to carefully consider your options and choose the path that best aligns with your goals and values.
In conclusion, becoming a US Air Force pilot requires a combination of academic excellence, physical fitness, and mental toughness. By meeting the basic requirements and choosing one of the five paths outlined above, you can increase your chances of success and achieve your dream of flying for the US Air Force.
What is the average salary for a US Air Force pilot?

+
The average salary for a US Air Force pilot varies based on rank and experience. However, according to the Air Force’s website, the average annual salary for a first lieutenant (the rank typically held by new pilots) is around $60,000.
How long does it take to become a US Air Force pilot?

+
The length of time it takes to become a US Air Force pilot varies depending on the path you choose. However, on average, it takes around 2-3 years to complete pilot training after being selected for the program.
What are the physical requirements for becoming a US Air Force pilot?

+
The physical requirements for becoming a US Air Force pilot include passing a physical fitness test, having a valid driver’s license, and meeting strict vision and hearing standards.



