7 Ways Air Force Refueling Planes Keep Jets Flying
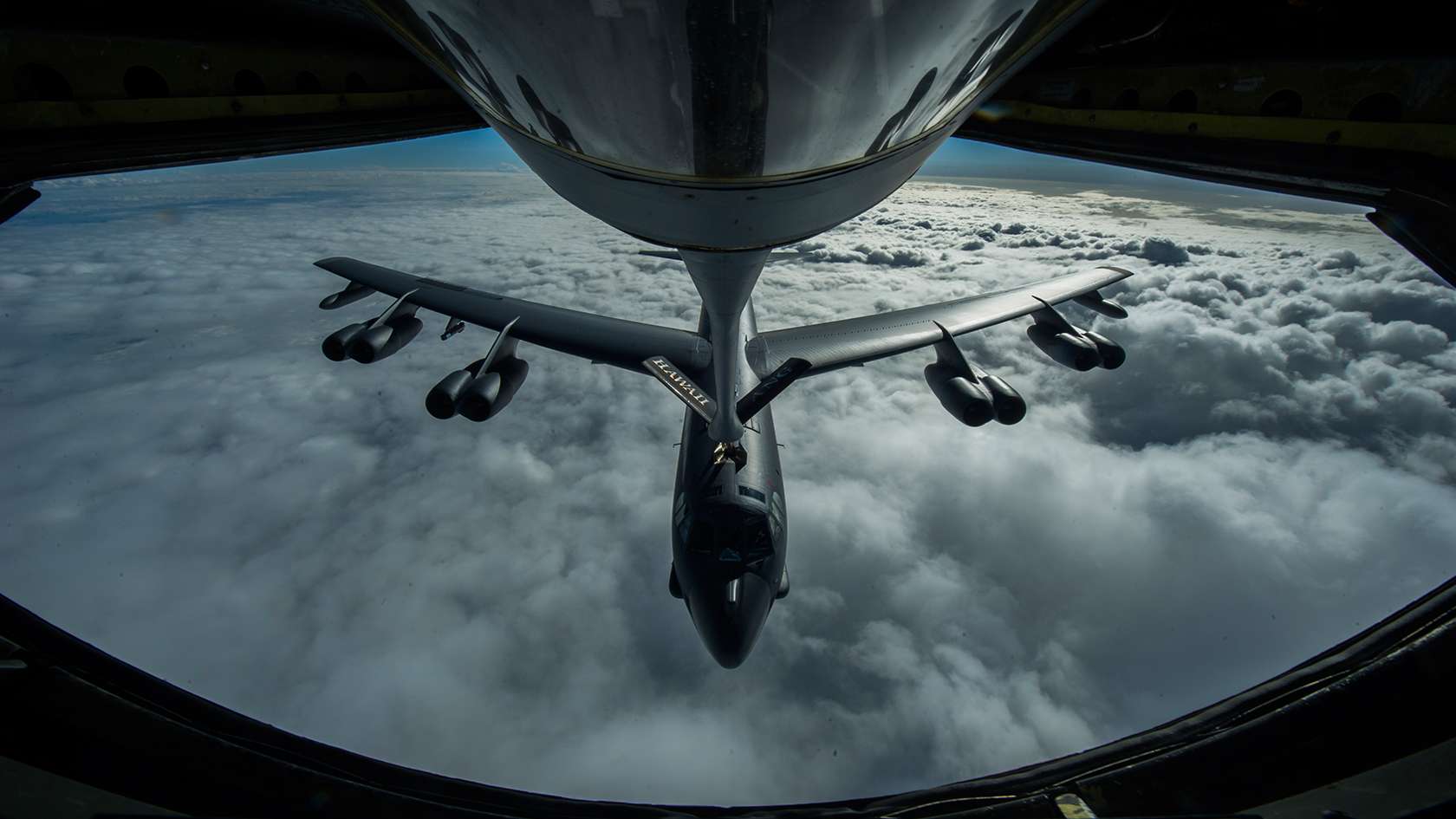

The Lifeline of Air Power: 7 Ways Air Force Refueling Planes Keep Jets Flying

Air Force refueling planes are the unsung heroes of air power, providing the vital link between takeoff and landing for military aircraft on long-range missions. These tankers, also known as aerial refueling aircraft, play a critical role in extending the range and endurance of fighter jets, bombers, and transport planes. In this article, we’ll explore the seven ways Air Force refueling planes keep jets flying.
1. Extending Range and Endurance

Aerial refueling enables aircraft to fly longer distances without having to land and refuel, which is crucial for military operations. By topping off their fuel tanks mid-air, fighter jets can stay in the combat zone for extended periods, and bombers can reach targets that would be out of range otherwise. This capability is particularly important for air-to-air combat and long-range strike missions.
2. Increasing Flexibility

Refueling planes provide aircrews with the flexibility to change their plans in response to changing circumstances. If a mission requires a detour or a longer-than-expected engagement, aerial refueling can ensure that the aircraft have enough fuel to complete the task. This flexibility is essential for military operations, where adaptability and responsiveness are key.
3. Enhancing Safety
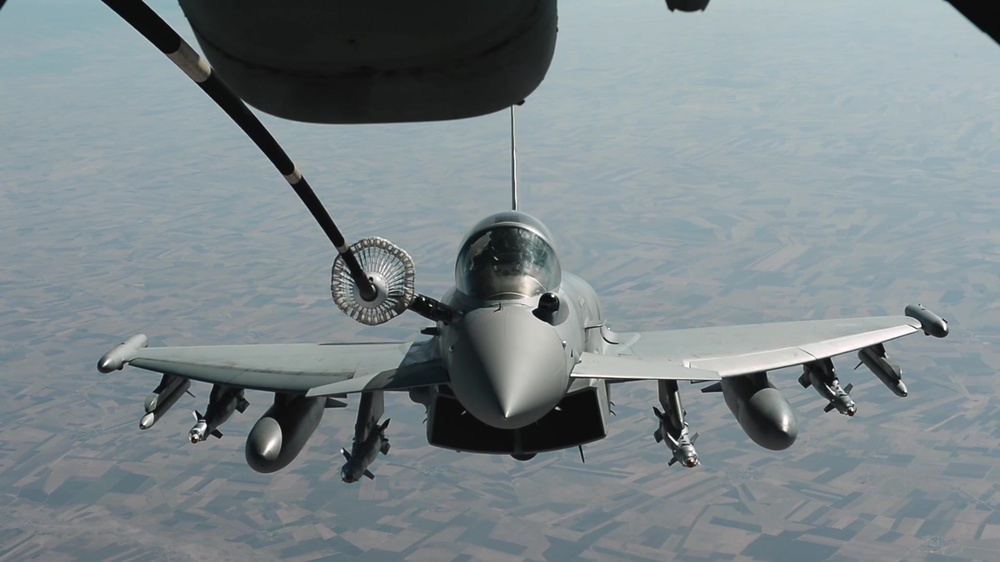

Aerial refueling reduces the risk of fuel exhaustion, which is a major safety concern for military aircraft. By refueling mid-air, aircrews can avoid the risks associated with low fuel states, such as engine failure or having to make emergency landings in hostile territory.
4. Supporting Large-Scale Operations
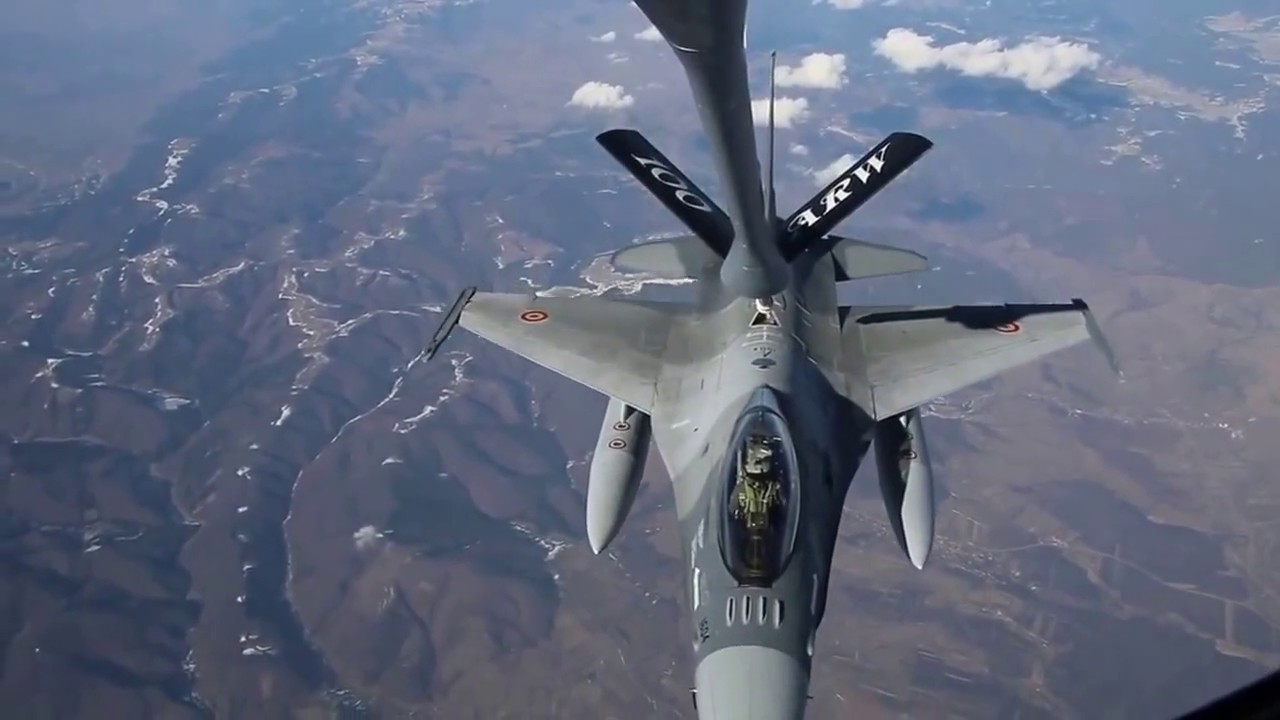

Air Force refueling planes play a critical role in large-scale military operations, such as exercises, deployments, and combat missions. By providing a reliable and efficient refueling capability, tankers enable multiple aircraft to operate simultaneously, which is essential for achieving strategic objectives.
5. Facilitating Rapid Deployment
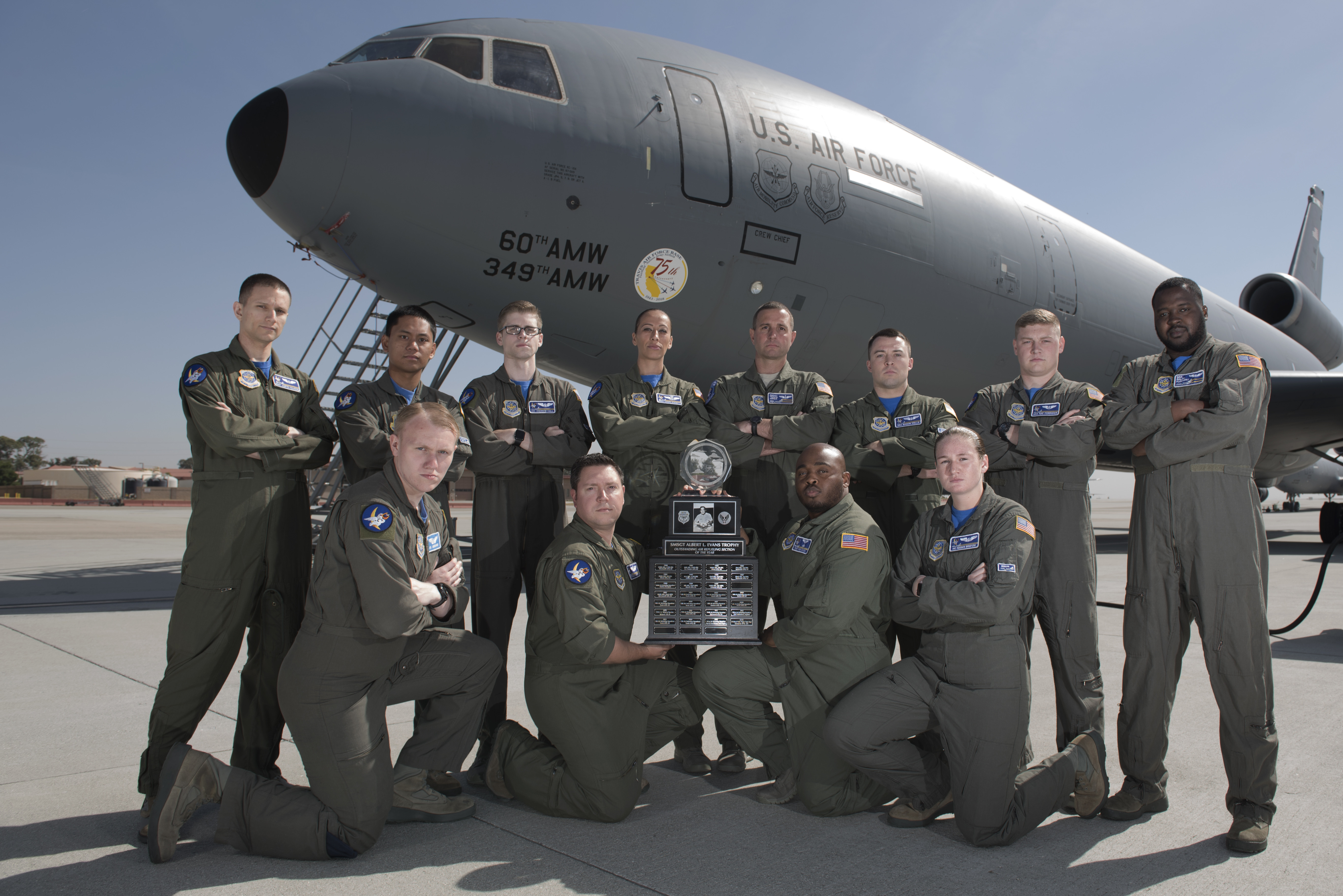

Aerial refueling enables rapid deployment of aircraft to crisis zones or conflict areas. By refueling in transit, aircrews can quickly respond to emerging threats or crises, which is critical for national security and crisis management.
6. Reducing Logistical Burden

Refueling planes reduce the logistical burden associated with supporting large-scale military operations. By eliminating the need for intermediate landings and refueling stops, aerial refueling simplifies the process of deploying and sustaining military aircraft.
7. Enhancing Interoperability
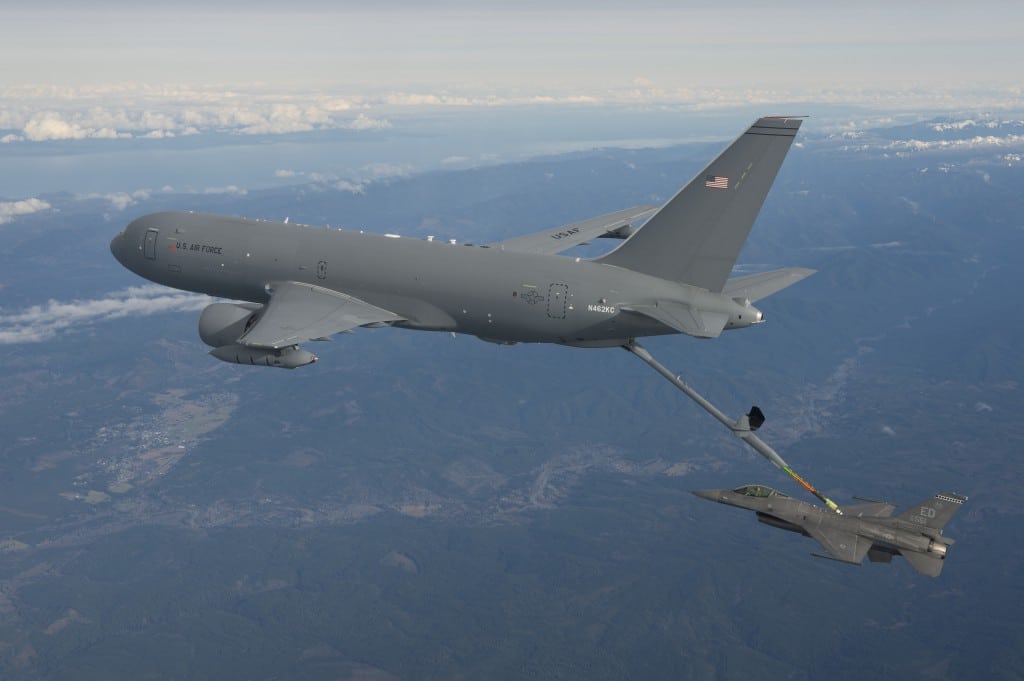

Air Force refueling planes can refuel aircraft from other nations, enhancing interoperability and facilitating coalition operations. This capability is essential for joint and combined operations, where multiple nations and services work together to achieve common objectives.
🚀 Note: The specific refueling techniques and procedures used by the Air Force are highly classified and subject to change. The information provided in this article is for general informational purposes only.
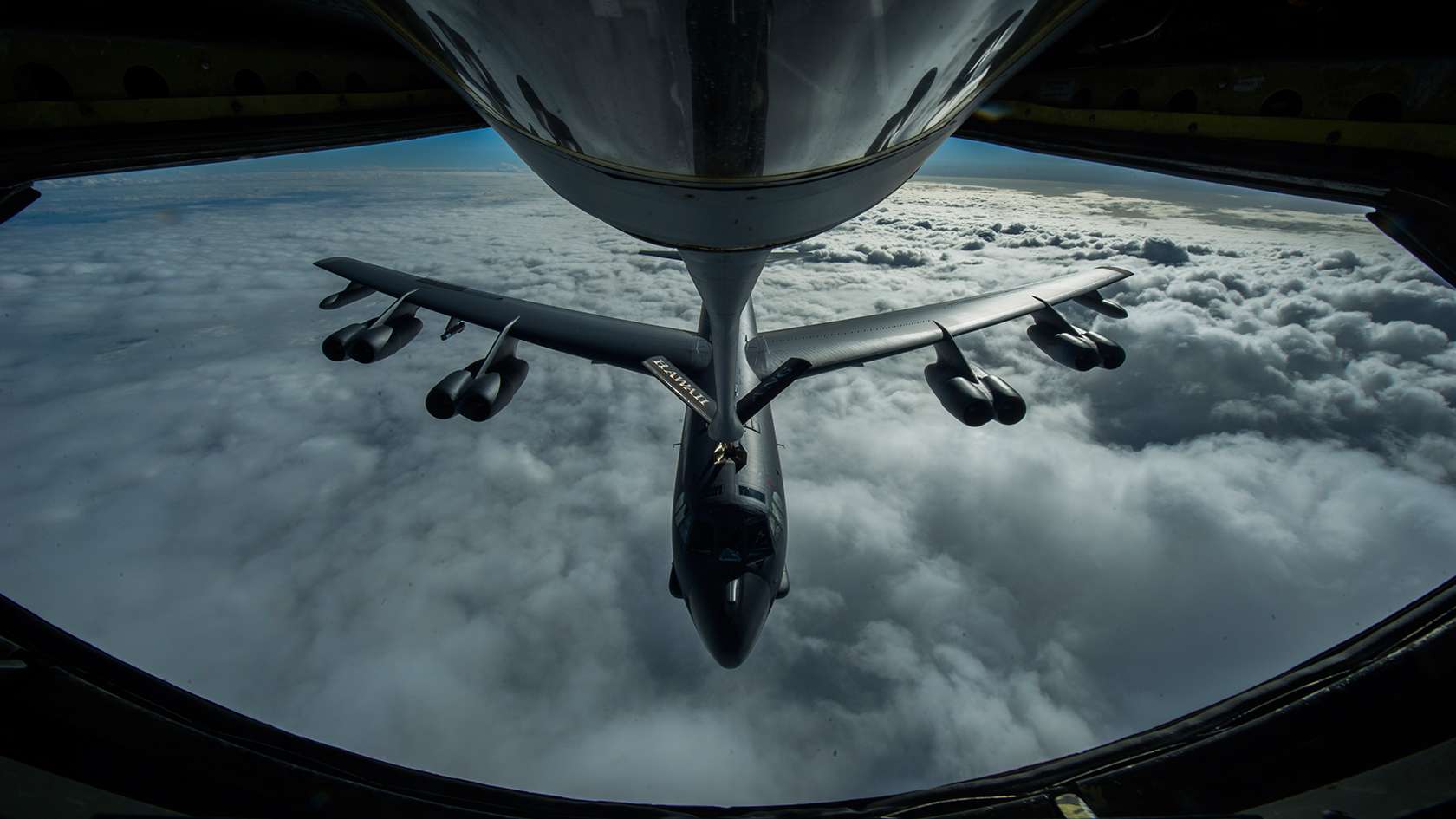
What is the primary role of Air Force refueling planes?

+
The primary role of Air Force refueling planes is to provide aerial refueling support to military aircraft, extending their range and endurance.
How do Air Force refueling planes enhance safety?

+
Aerial refueling reduces the risk of fuel exhaustion, which is a major safety concern for military aircraft. By refueling mid-air, aircrews can avoid the risks associated with low fuel states.
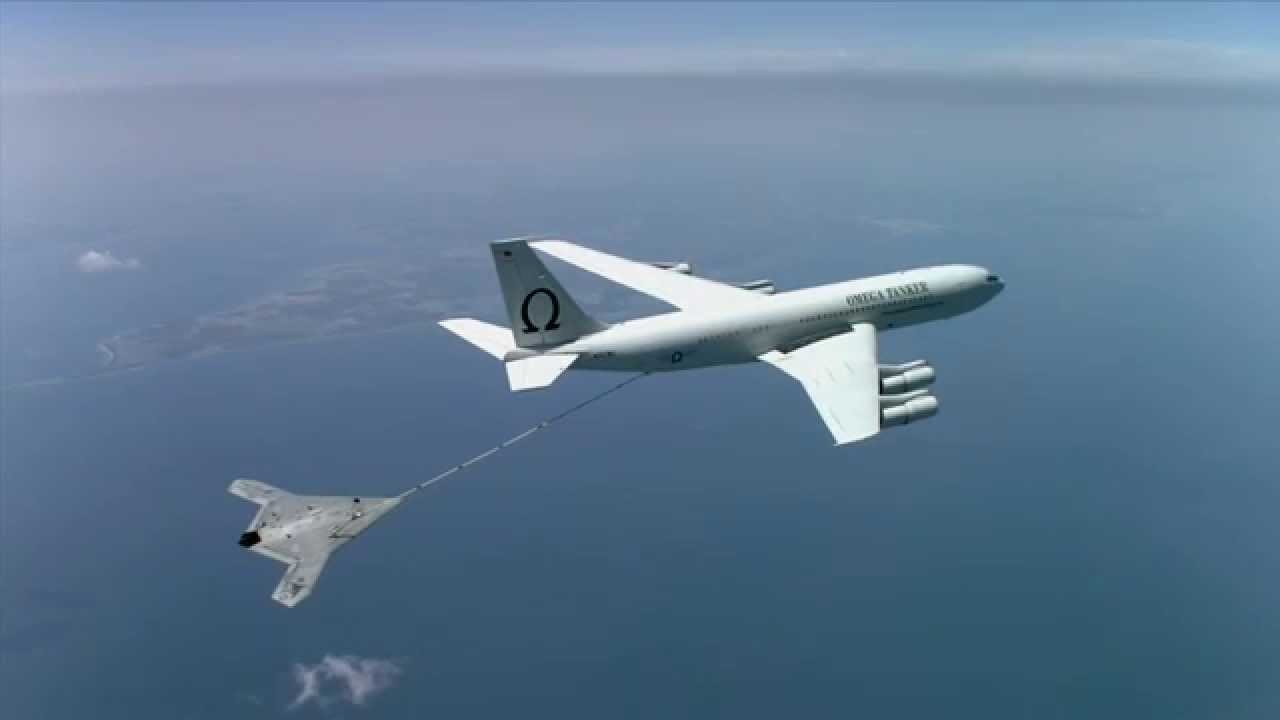
Can Air Force refueling planes refuel aircraft from other nations?

+
Yes, Air Force refueling planes can refuel aircraft from other nations, enhancing interoperability and facilitating coalition operations.
In summary, Air Force refueling planes play a vital role in supporting military aircraft, extending their range and endurance, increasing flexibility, enhancing safety, supporting large-scale operations, facilitating rapid deployment, reducing logistical burden, and enhancing interoperability. These tankers are the backbone of air power, providing the critical refueling capability that enables military aircraft to operate effectively and efficiently.