Electrifying Image: A Picture of Electric Currents
Unlocking the Secrets of Electric Currents
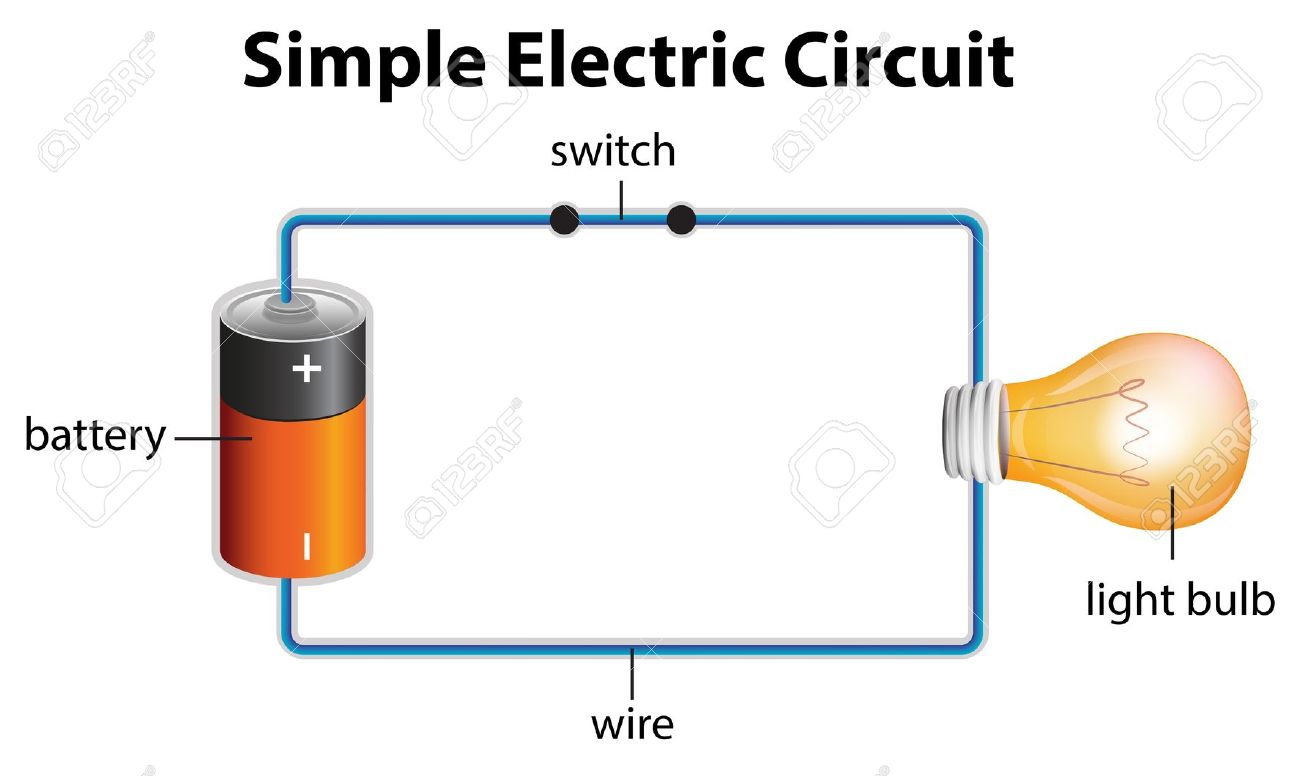
Electric currents are a fascinating phenomenon that surrounds us in our daily lives. From the simplest household appliances to the most complex industrial machinery, electricity plays a crucial role in making our lives easier and more convenient. But have you ever stopped to think about what electric currents actually are? In this article, we will delve into the world of electric currents and explore the intricacies of this powerful force.
What are Electric Currents?
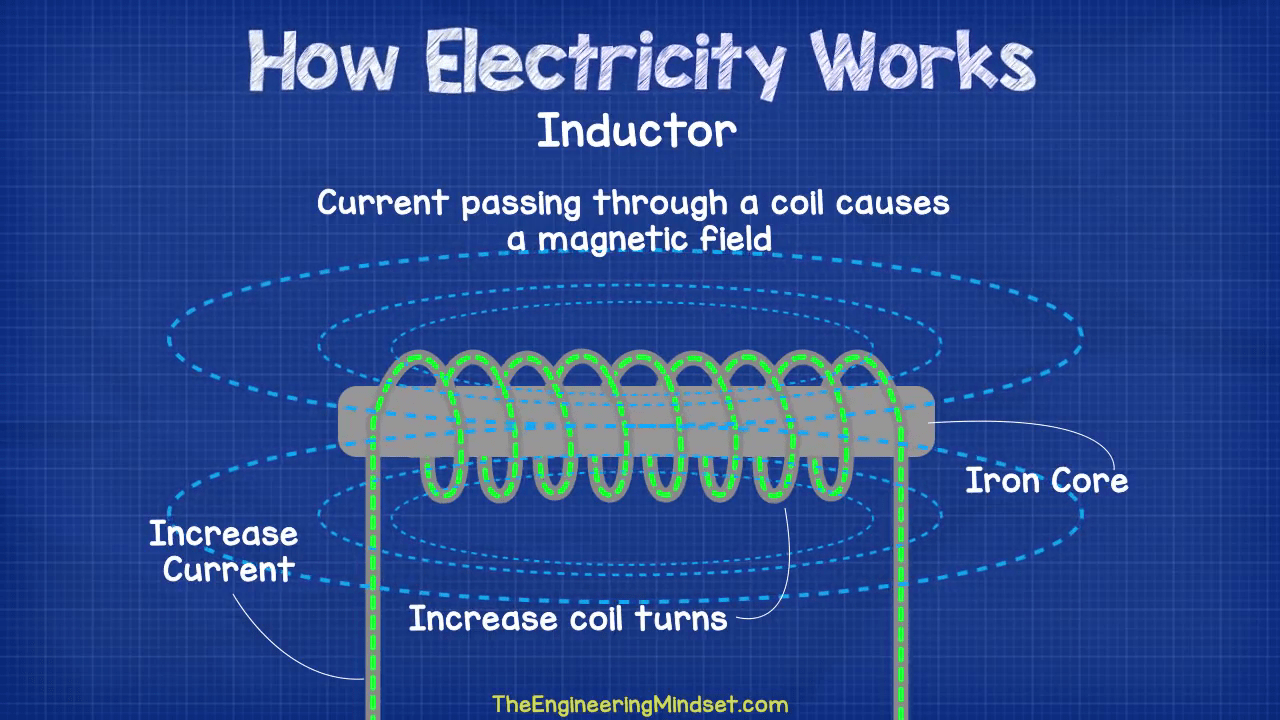
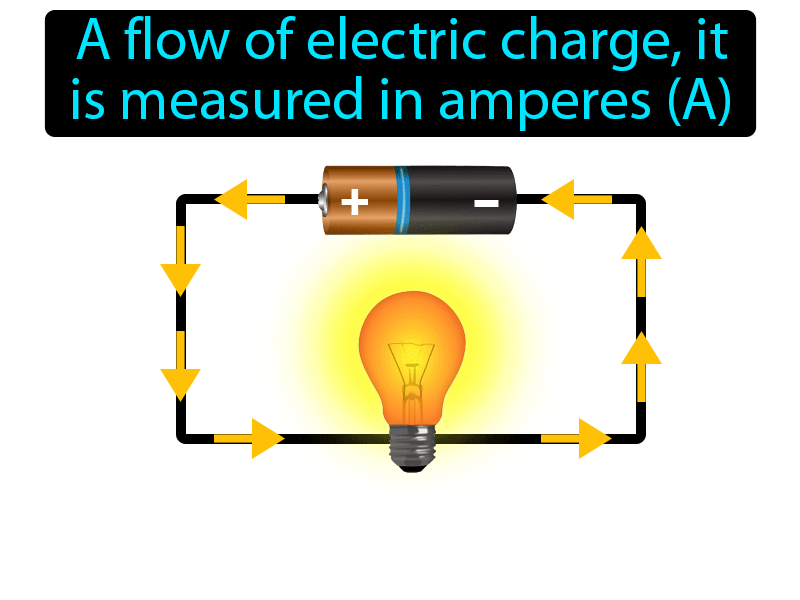
Electric currents are the flow of electrons through a conductor, such as a wire. This flow of electrons is what we commonly refer to as electricity. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), and the strength of the current depends on the number of electrons flowing through the conductor. The voltage, on the other hand, is the force that drives the electrons through the conductor and is measured in volts (V).
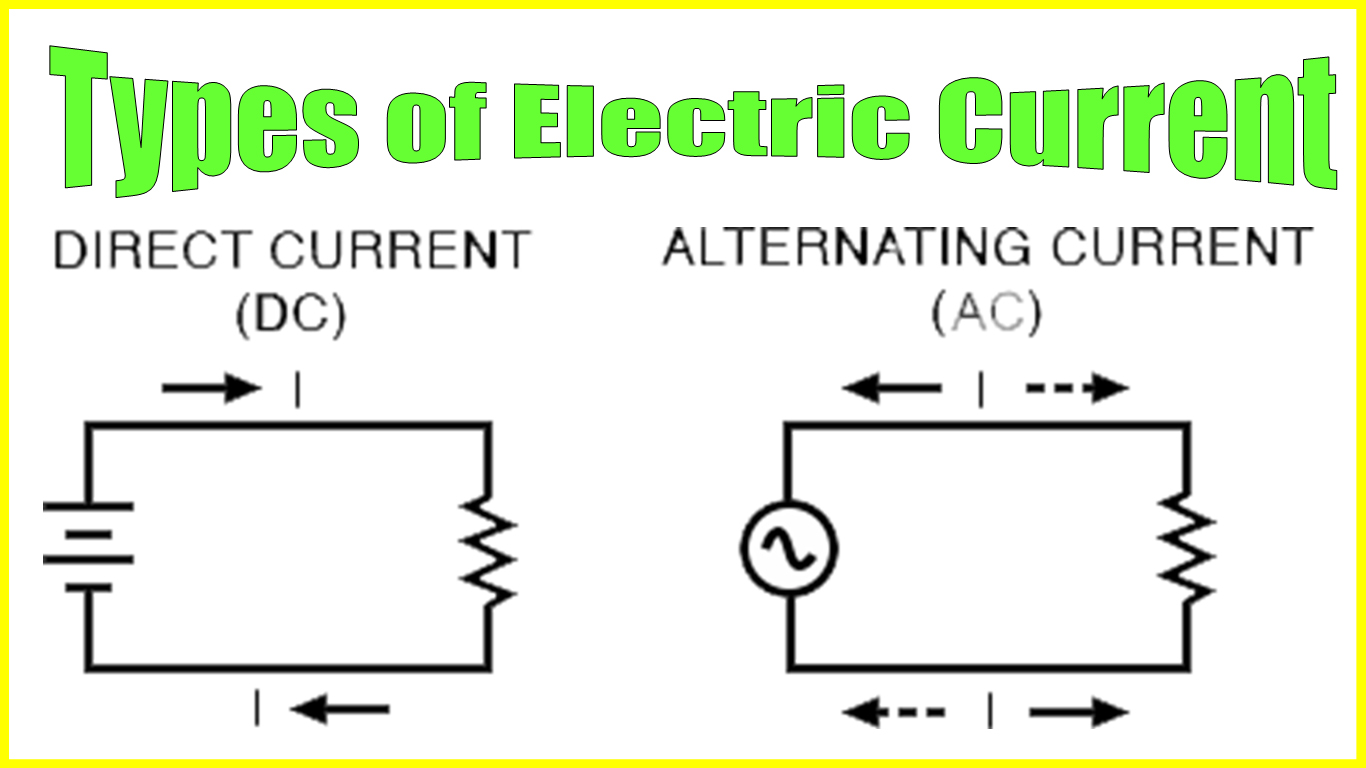
Types of Electric Currents

There are two main types of electric currents: direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC).
- Direct Current (DC): DC flows in one direction only, from positive to negative. It is commonly used in electronic devices, such as smartphones and laptops.
- Alternating Current (AC): AC changes direction periodically, oscillating between positive and negative. It is commonly used in households and industries for powering appliances and machinery.
How Electric Currents Work
Electric currents work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When a conductor is placed in a magnetic field, an electric current is generated. This is because the magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the conductor, causing the electrons to flow.
The flow of electric current is determined by the following factors:
- Resistance: The opposition to the flow of electrons, measured in ohms (Ω).
- Voltage: The force that drives the electrons through the conductor.
- Current: The flow of electrons, measured in amperes (A).
Applications of Electric Currents
Electric currents have a wide range of applications in our daily lives. Some of the most common applications include:
- Powering Household Appliances: Electric currents are used to power household appliances, such as refrigerators, air conditioners, and washing machines.
- Industrial Applications: Electric currents are used in industries for powering machinery, such as motors and generators.
- Transportation: Electric currents are used in electric vehicles, such as cars and buses.
💡 Note: Electric currents can be hazardous if not handled properly. It is essential to take safety precautions when working with electric currents to avoid electrical shock and injury.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electric currents are a fundamental aspect of our daily lives. Understanding the intricacies of electric currents can help us appreciate the importance of electricity in our lives. From powering household appliances to industrial applications, electric currents play a vital role in making our lives easier and more convenient.
What is the difference between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC)?

+
Direct current (DC) flows in one direction only, while alternating current (AC) changes direction periodically.
What is the unit of measurement for electric current?

+
The unit of measurement for electric current is amperes (A).
What is the principle behind electric currents?

+
Electric currents work on the principle of electromagnetic induction.